This is my week 2 lab report that will give a tutorial on how to login to the ieng6 account
Installing VScode
- Download VSCode for your OS, in this report, I will be using a MAC OS. Use this link to download VSCode
- After you finish downloading VSCode, open the application. Your screen should look someting like this
Remotely Connecting
-
Now that you have VSCode set up, open up the terminal. I recommend splitting the terminal, so you can work on your ieng6 account and your own local account. You can do this my clicking Terminal in the top left corner (for Mac), new terminal, and right clicking your terminal to split the terminal.
-
To remotely connect, you will need your ieng6 email and a password that you will create on the server. You can use this document to change your password for your course-specific account.
-
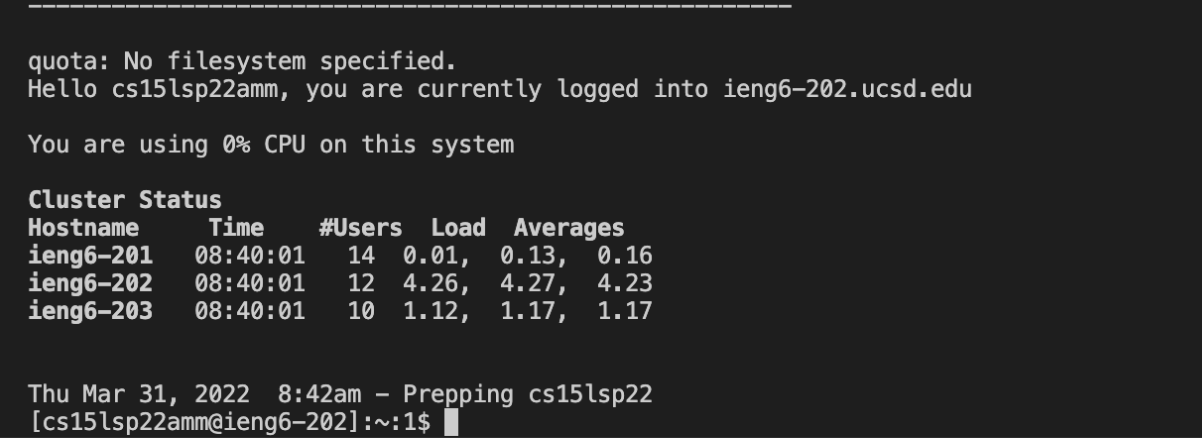
For my example, my account username is cs15lsp22amm@ieng6.ucsd.edu, and I have my password changed. I will use the ssh command to finally remotely connect. If you are using Windows, you will need to download this to utilize the ssh command.
-
Your terminal should look something like this
Trying Some Commands
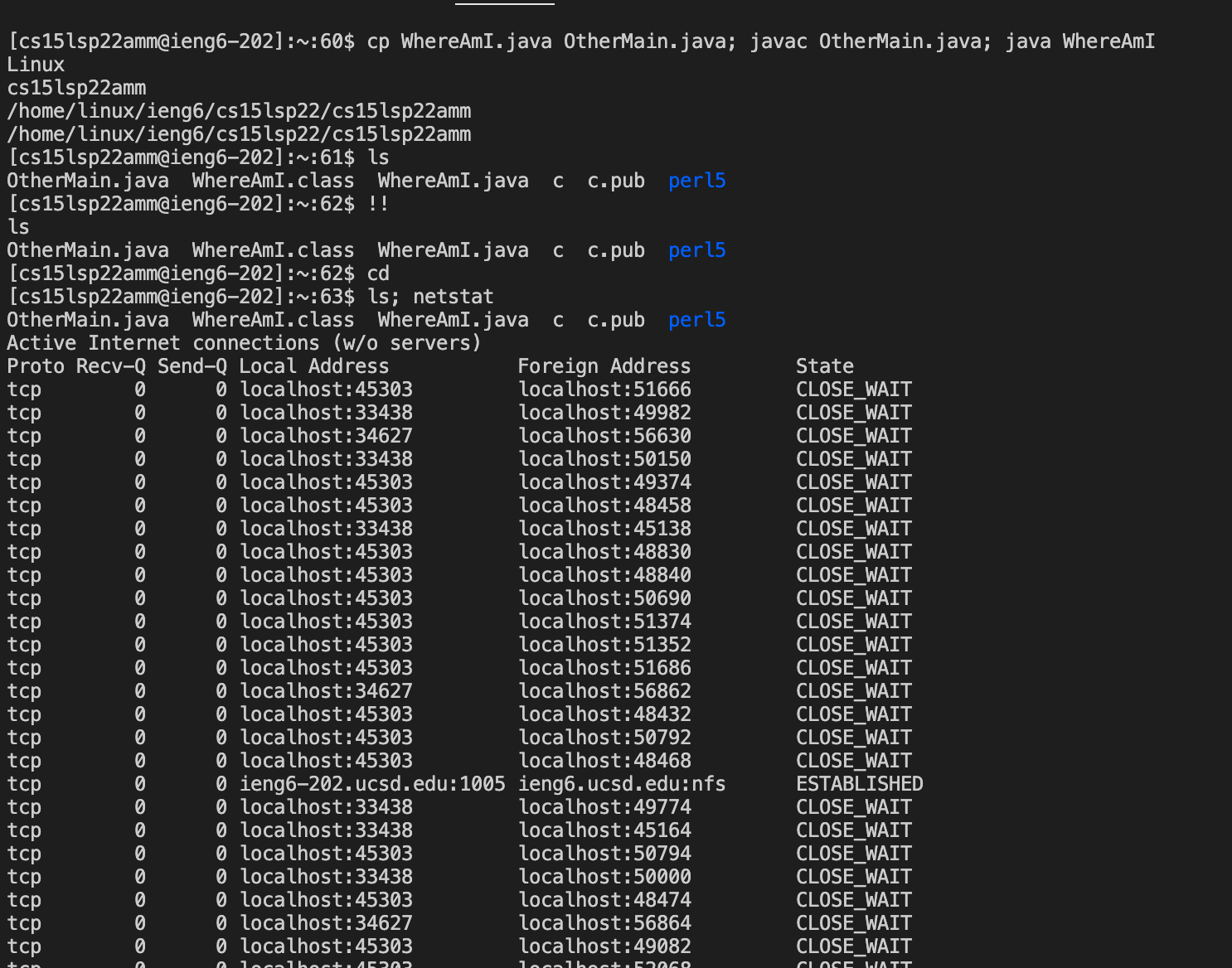
- Here are some commands that you can try after connecting remotely. You may also just Google Unix Commands to find some commands to test. Here’s a website with some basic unix commands.
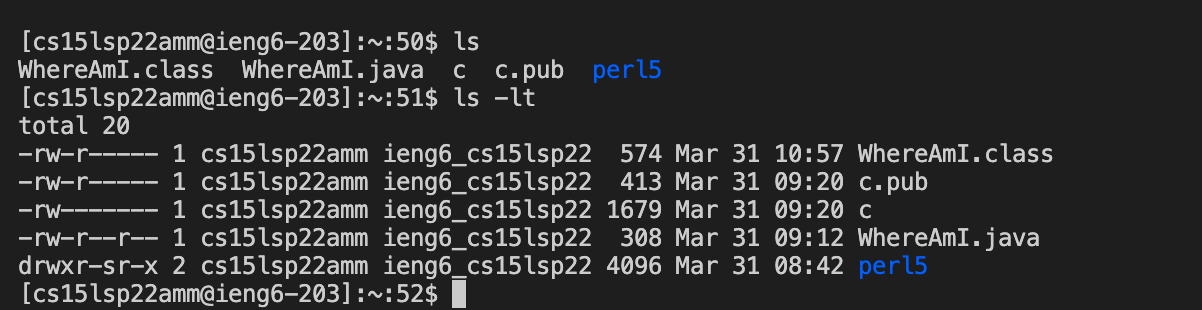
- In my example, I use ls and ls -lt. The third picture below shows the output I got after running these commands.
Moving Files with scp
- The SCP unix command means secure copy protocol. This is where I mentioned in remotely connecting that splitting the terminal will be beneficial. You want to have your local account and the other for your ieng6 account.
- You want to by entering **scp
** in your own local account. In my example here 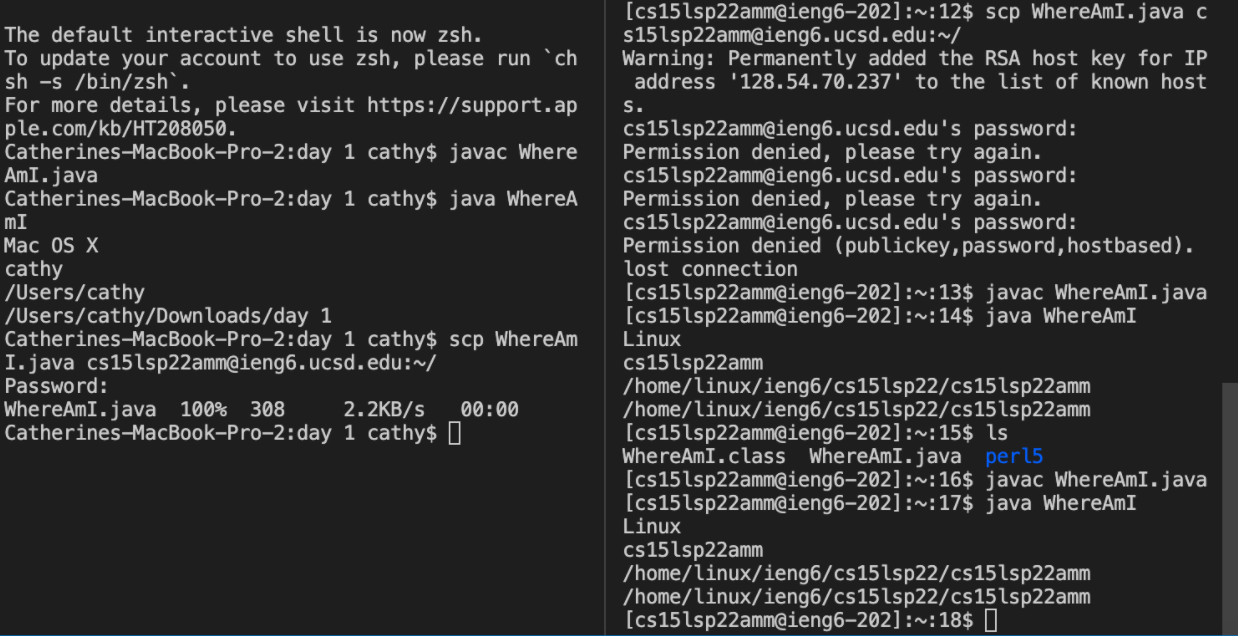, you can see that I want to copy over my file WhereAmI.java. It is going to prompt you to enter your password to youe ieng6 account just for vertification. So just enter your password. - Here is an example of a file that you can use an example for moving files with scp. I created this file WhereAmiI.java.
public class WhereAmI {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(System.getProperty("os.name"));
System.out.println(System.getProperty("user.name"));
System.out.println(System.getProperty("user.home"));
System.out.println(System.getProperty("user.dir"));
}
}
- And just like that you have copied over a file.
Setting a SSH Key
-
The reason that we want to set up a SSH Key is because it saves time so that we don’t have to input a password every time we try to login. It gets time consuming to always have to enter our password and can sometimes interrupt the tasks that we are doing.
-
The first thing is you are going to want to type ssh-keygen into the terminal. Then you will be asked to enter a file to save the key. You are going to want to enter **(/Users/
/.ssh/id_rsa): /Users/ /.ssh/id_rsa**. However, replace the user-name portion with your user. -
Next it is going to ask you to enter a passphrase, just click enter and don’t enter anything for both times it asks you. It will complete creating an SSH Key and generate your key’s randomart image. Every key’s randomart image is different for each person. Mine looks like this
-
Now, when you login to your ieng6 account, it will not ask you to enter a password
Optimizing Remote Running
- Some tips that I learned that were helpful in optimizing time was using the semi-colon so you would be able to run multiple commands in one line. This would prompt the commmands all on that one line to run at the same time, which saves a lot of time. (;)
- The !! command also helps by running the last unix command that you called. This saves time, so you don’t need to type out the previous line all over again.
- Another tip is using the up arrow on your keyboard. It allows you to see the last command that you call, which is similar to the “!!” command but both work well in optimizing the remote running time.